JPA를 이용해서 RDB에 공간정보 저장하기
개요
이번 포스팅에서는 JPA를 이용해서 MySQL에 위치정보를 저장하는 법에 대해서 다뤄보도록 하겠다.
공간 정보(Geometry 타입)?
MySQL(사실, 다른 RDB에서도) 에서는, GPS좌표나 다각형과 같은 공간/기하 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 Geometry 타입을 제공한다.
MySQL과 같은 경우 아래 목록의 타입들을 제공한다
| 데이터 타입 | 설명 |
| Point | 좌표 공간에서 한 지점의 위치를 표시 [ Ex : Point(10,10) ] |
| LineString | 다수의 점을 연결해주는 선분 [ Ex : LINESTRING(10 10, 20 25, 15 40) ] |
| Polygon | 다수의 선분들이 연결되있는 다각형 [ Ex : POLYGON(10 10, 10 20, 20 20, 20 10, 10 10) ] |
| Multi-Point | 다수개의 점들의 집합 [ Ex : MULTIPOINT(10 10, 30 20) ] |
| Multi-LineString | 다수개의 선분들의 집합 [ Ex : MULTILINESTRING((10 10, 20 25, 15 40), (50 50, 85 105, 120 160)) ] |
| Multi-Polygon | 다수개의 다각형들의 집합 [ Ex : MULTIPOLYGON((10 10, 10 20, 20 20, 20 10, 10 10), (10 10, 10 20, 20 20, 20 10, 10 10)) ] |
| GeomCollection | 모든 공간데이터들의 집합 [ Ex : GEOMCOLLECTION(POINT(10,10), LINESTRING(10 10, 20 25, 15 40)) ] |
이제 이러한 공간정보를 스프링에서 제공하는 ORM인 JPA(+hibernate)를 이용해서 저장해보는 예제를 작성해보자.
해당 예제에서는 Point(위도/경도) 정보를 저장/불러오는 예제를 다루도록 하겠다.
예제
먼저 스프링 프로젝트를 만들고 아래와 같이 Maven에 의존성을 추가해주자.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.semtax.geometryexample</groupId>
<artifactId>geometryexample</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<version>1.4.199</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-spatial</artifactId>
<version>5.3.10.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.gavlyukovskiy</groupId>
<artifactId>p6spy-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.19</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.vorburger.mariaDB4j</groupId>
<artifactId>mariaDB4j</artifactId>
<version>2.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.0</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
공간 데이터 저장을 위해 hibernate의 hibernate-spatial 라이브러리를 의존성으로 추가했다.
해당 라이브러리의 버전은 스프링부트의 hibernate 버전에 맞춰주면 된다.
다음으로 아래와 같이 application.properties 를 작성해준다.
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=10
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.hibernate.use-new-id-generator-mappings=false
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.jdbc.lob.non_contextual_creation=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.spatial.dialect.mysql.MySQL56InnoDBSpatialDialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
server.port=45000
먼저 MySQL 8 이상을 쓰는 경우 위와 같이 datasource.url을 작성해야 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
(기본적으로 SSL 통신을 사용함 + UTC 시간 지정이 필요)
그리고, JPA 구현체로 hibernate를 사용하겠다는 설정과, 기타 설정들을 지정해준다.
다음으로 아래와 같이 위치정보가 포함된 Entity 객체를 작성해준다.
package main.java.entity;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import java.util.Objects;
@Entity
public class PointEntry {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private Point point;
public PointEntry() {
}
public PointEntry(Point point) {
this.point = point;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Point getPoint() {
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point) {
this.point = point;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
PointEntry that = (PointEntry) o;
return Objects.equals(id, that.id) &&
Objects.equals(point, that.point);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, point);
}
}
그리고 나서, 위에서 선언한 엔티티(개체)에 대한 Repository 를 작성해준다.
package main.java.repositories;
import main.java.entity.PointEntry;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface PointEntryRepository extends JpaRepository<PointEntry, Long> {
}
다음으로, 실제 위치정보를 저장하고 불러오는 컨트롤러들을 작성해준다.
package main.java.controller;
import main.java.entity.PointEntry;
import main.java.repositories.PointEntryRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
PointEntryRepository pointEntryRepository;
@GetMapping("/")
public List<PointEntry> mainPage(){
return pointEntryRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/insert")
public String insertPage(){
Random r = new Random();
PointEntry pointEntry = new PointEntry(new Point(r.nextDouble(),r.nextDouble()));
pointEntryRepository.save(pointEntry);
return "success";
}
}
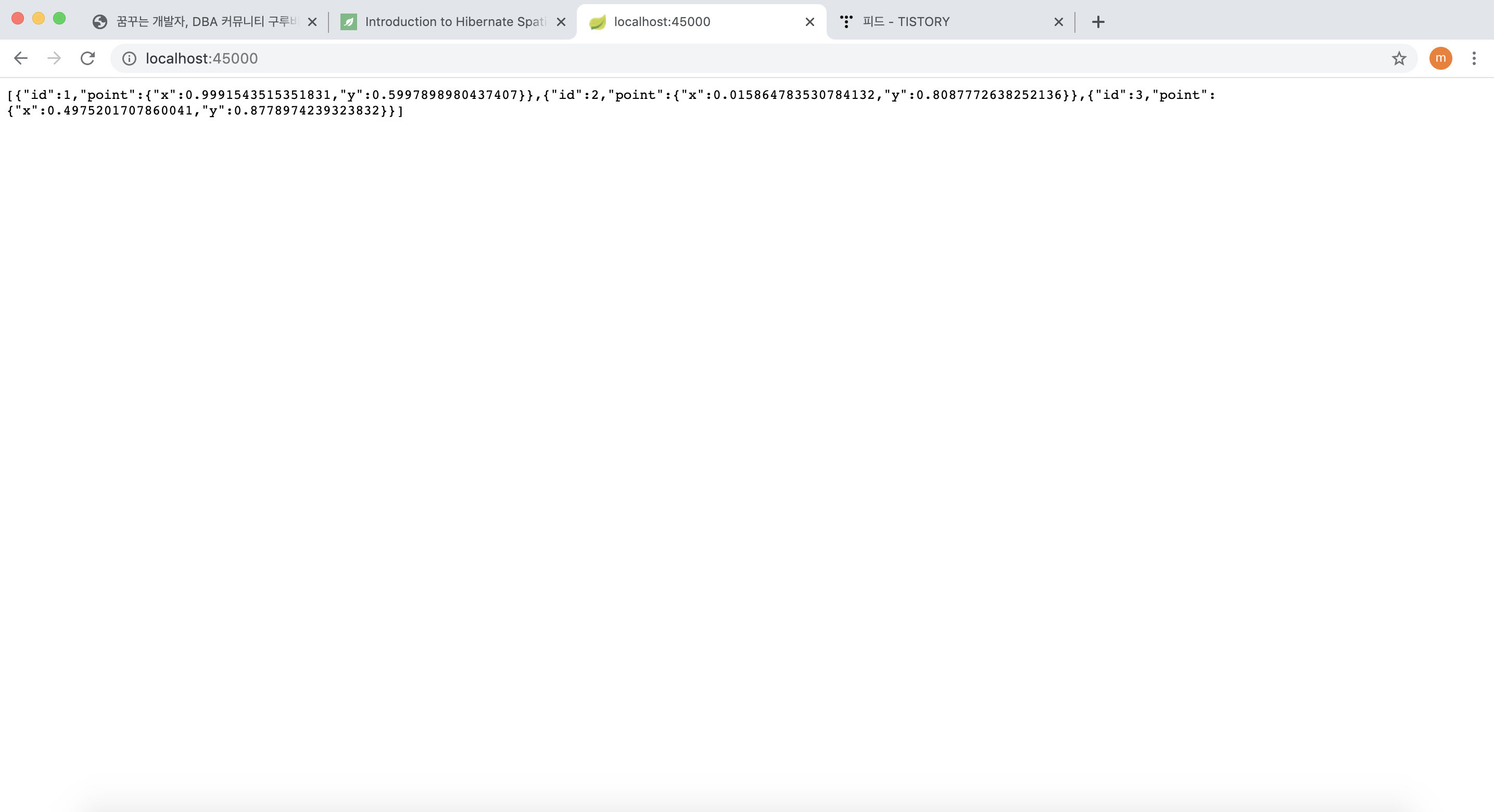
위의 컨트롤러에서는, "/insert" 페이지를 통해 랜덤으로 위도/경도 정보를 저장하고 "/" 페이지를 이용해서 지금까지 저장한 모든 위치정보(위도/경도) 들을 출력 해주는 역할을 수행하게 된다.
마지막으로 Main 함수를 아래와 같이 작성해준다.
package main.java;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringGeometryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringGeometryExample.class, args);
}
}
이제 실제로 위에서 작성한 예제를 실행해보도록 하자.
실행 결과
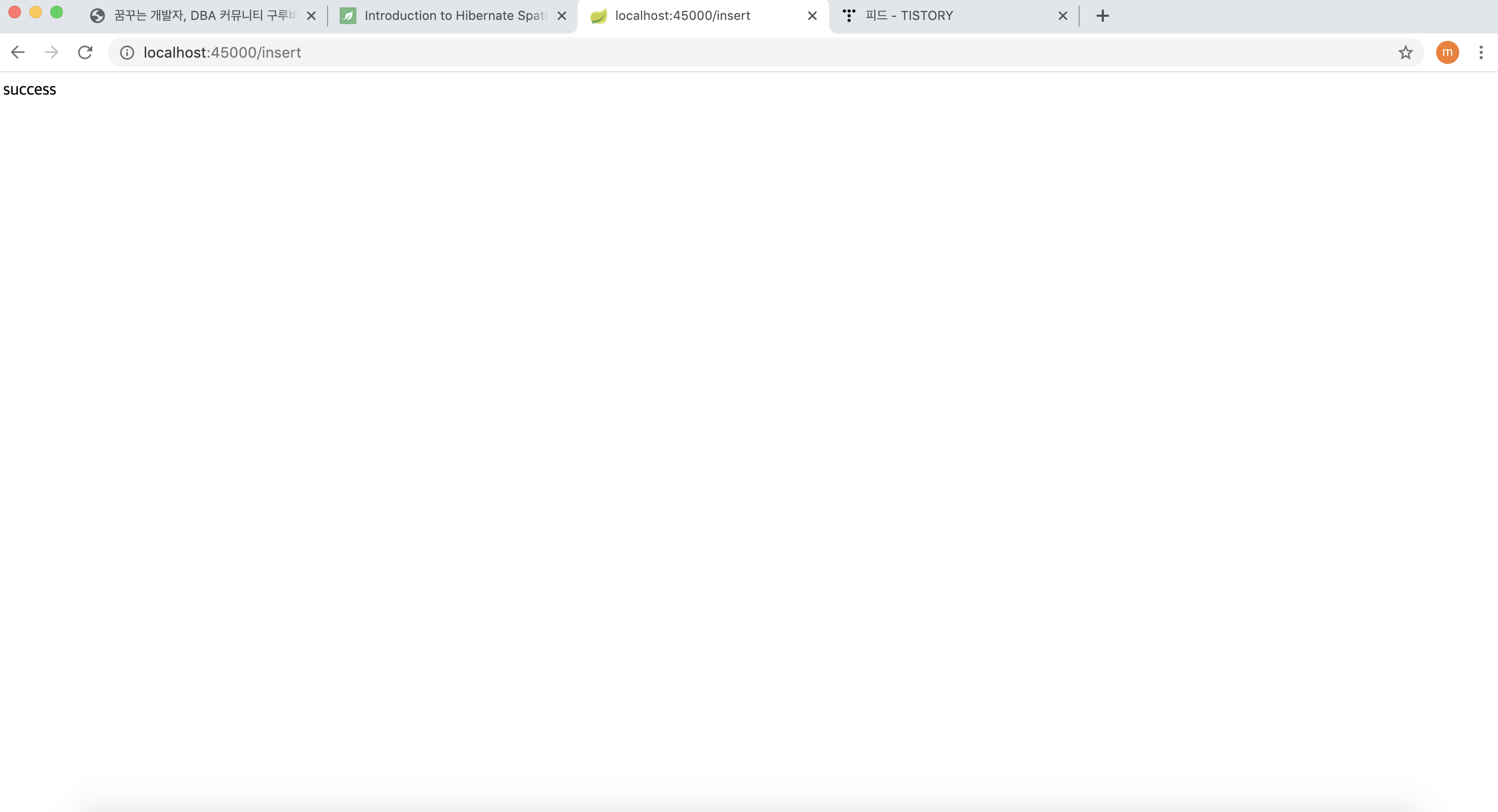
먼저 아래와 같이 /insert 페이지를 연속적으로 방문해서 위도/경도 데이터를 넣어주자.
그리고 아래 페이지를 방문하면 위도/경도 목록들을 얻을 수 있다.